We've now learned about diodes, photons and electroluminescence.
Wow!
Now let's learn about something called LEDs.
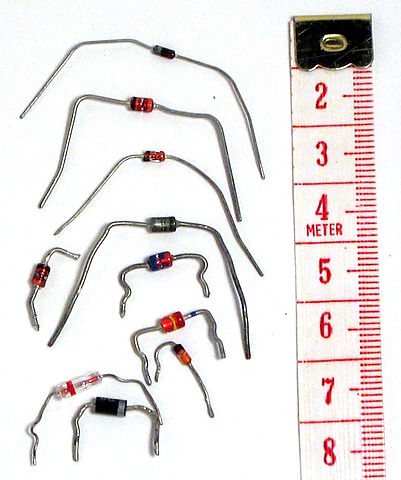
LED stands for light emitting diode.
Remember that a diode is a special thing you run electricity through.
When you put electricity through an LED, it shoots off photons,
which are tiny little light particles.
And the photons make the diode light up, using electroluminescence,
which means it gives off light when electricity goes through it.
LEDs can be made in just about every color, and unlike a light bulb they won't burn out!

(from: wikipedia - light-emitting diode)
Kid Facts - Blast from the past: Electrical Box