We just learned about the Poppet Valve, and we learned about the Ball Valve before that.
There are lots of different Valve Types out there that are made for different reasons.
A Globe Valve has a body that is shaped sort of like a globe, and has a disc that goes up and down to plug the hole and stop the flow of liquid or gas.

(from: wikipedia - globe valve)
A Butterfly Valve has a circle shaped disc in the middle that spins to open or close.

(from: wikipedia - butterfly valve)
A Gate Valve has a gate that goes up and down to open or close the hole.

(from: wikipedia - gate valve)
A Check Valve is a type of valve that stays closed unless the liquid or gas pushes hard enough to open it, and then it will close again using something like a spring.
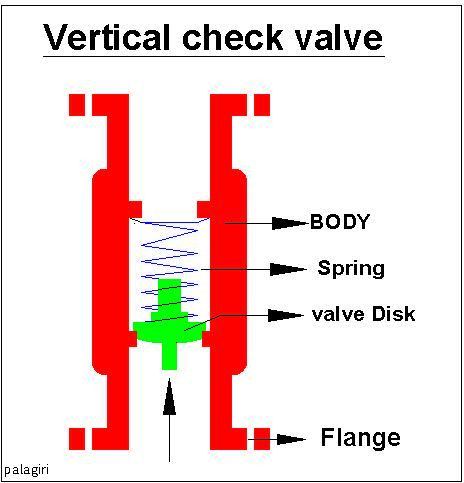
(from: wikipedia - check valve)
A Control Valve is a valve that is controlled by a computer to tell it to open a little or a lot, so that it can control the amount of liquid or gas that is coming through.

(from: wikipedia - control valve)
Valves can have have a lot more than just two holes or ports also.
Many valves have three or four ports, and some have even more!

(from: wikipedia - four way valve)
There are a lot more types of valves out there. Pretty much any way you can think of to open or close a pipe, someone has made a valve for it.
Kid Facts - Blast from the past: V-2 Rocket