We just learned about how scientists can look at guns with
Forensic Firearm Examination to see who committed a crime.
Another part of forensic science is
Forensic Anthropology.
This is the science of looking at the bones of a person and trying to figure out what happened.
Sometimes this is used in archeology for bones that are hundreds or thousands of years old.
Other times it can be used by police when they find some bones, to try and figure out who the person was.
Scientists can look at teeth to see how old the person was, or the length of their arm or leg bones, or even the size of their skull.
They can even look at the hip bones of a person to see if they were a man or a woman.
Sometimes this helps solve a crime if they find an old skeleton, and they don't know who the person was when they were alive.
If they figure out who it was, they can look for marks on the bones, to maybe tell how they died.
They can also look at the teeth, and sometimes match them up with x-rays from a dentist office to see if they can figure out who it was.
It might seem a little scary or creepy, but by using science with old bones we can solve crimes and make sure the bad guys don't get away!

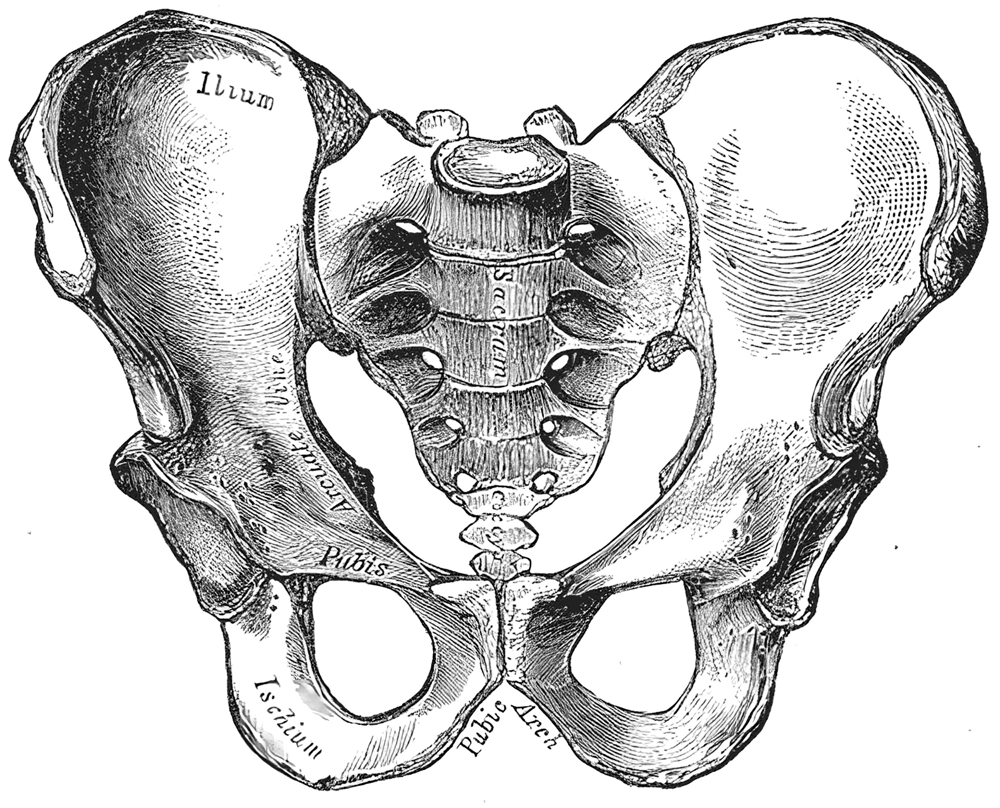
(from: wikipedia -
forensic anthropology)
Kid Facts - Blast from the past: Rocket Propellant Tank








