We just learned that
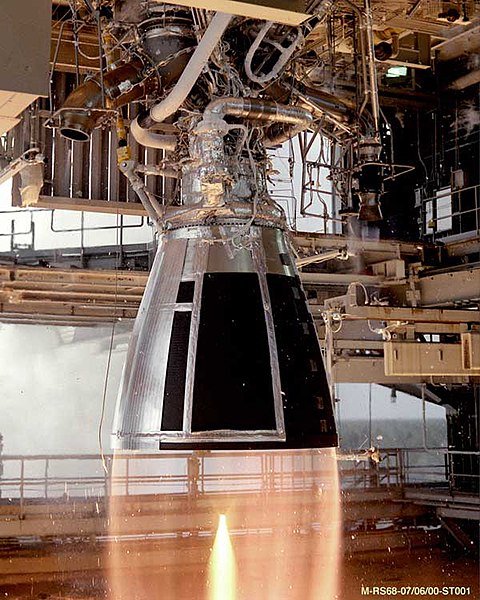
Rocket Propellant is the fuel that pushes a rocket along, and they can be solid, liquid or gas.
Solid Rocket Propellants are made up of a few different types of chemicals all mixed together.
Some parts of the mixture are to make a big explosion that will push the rocket along.
Other parts are soft and sticky almost like dough that help hold all the explosive stuff together.
Different chemicals will make bigger explosions or burn longer or hotter, so the rocket scientists have to pick the right kind of propellant for the right job.
Solid propellants are easier to store than liquid or gas, because they don't leak out much.
Also some liquid or gas propellants can eat away at the rocket tanks or rubber seals holding it in.
Solid propellants are heavier than liquid or gas, and a rocket with the same amount of liquid or gas would get more power and weigh less.
Sometimes the solid propellants can even get cracks or bubbles in the mix.
If you think about it like a big ball of playdough, any of the parts that aren't smooth, or any folds in the middle that have air pockets would cause problems.
The NASA space shuttle used two rockets with solid propellant, called the "Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs)"
At the time they were the most powerful solid rocket motors ever flown, and the two of them together weighed 2.6 million pounds.
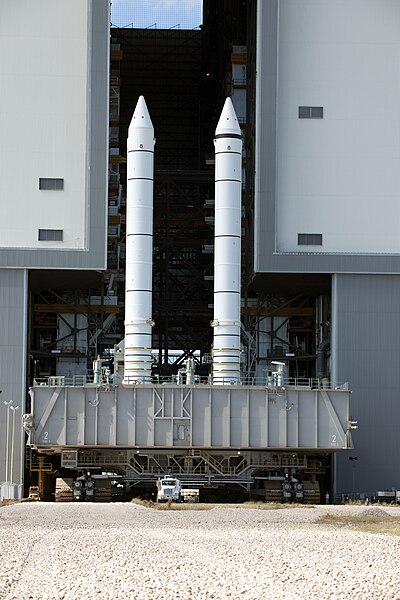

(from: wikipedia -
space shuttle solid rocket booster)
Kid Facts - Blast from the past: Skivving Machine